
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1922
1922번: 네트워크 연결
이 경우에 1-3, 2-3, 3-4, 4-5, 4-6을 연결하면 주어진 output이 나오게 된다.
www.acmicpc.net
문제
도현이는 컴퓨터와 컴퓨터를 모두 연결하는 네트워크를 구축하려 한다. 하지만 아쉽게도 허브가 있지 않아 컴퓨터와 컴퓨터를 직접 연결하여야 한다. 그런데 모두가 자료를 공유하기 위해서는 모든 컴퓨터가 연결이 되어 있어야 한다. (a와 b가 연결이 되어 있다는 말은 a에서 b로의 경로가 존재한다는 것을 의미한다. a에서 b를 연결하는 선이 있고, b와 c를 연결하는 선이 있으면 a와 c는 연결이 되어 있다.)
그런데 이왕이면 컴퓨터를 연결하는 비용을 최소로 하여야 컴퓨터를 연결하는 비용 외에 다른 곳에 돈을 더 쓸 수 있을 것이다. 이제 각 컴퓨터를 연결하는데 필요한 비용이 주어졌을 때 모든 컴퓨터를 연결하는데 필요한 최소비용을 출력하라. 모든 컴퓨터를 연결할 수 없는 경우는 없다.
시간 복잡도 분석
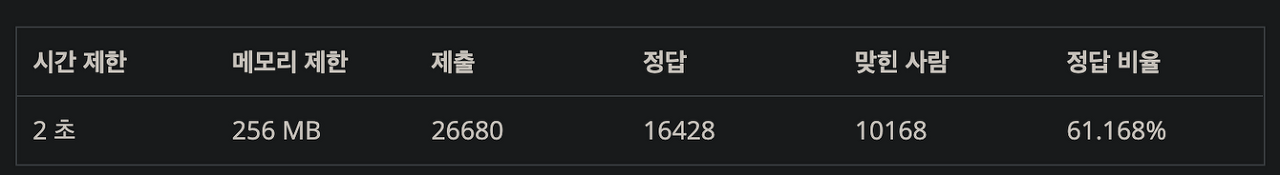
1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000
1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000
M줄에 각 N을 연결한다.
정점끼리 하나의 간선으로만 연결되는 최소 비용을 고르는 문제입니다.
최악의 경우
N이 M개 중 하나를 고르고
N-1이 M-1개 중 하나를 고르고
N-2이 M-2개 중 하나를 고르고
…
1,000이 99,000개 중 하나를 고르니
(1 * (M - 1)) * (1 * (M - 2)) …
이므로 $O(M^N)$이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
지수 시간 보다 나쁜 시간 복잡도입니다
때문에 이런식으로 구현하면 곧바로 시간 초과입니다.
때문에 저는 사이클이 없는 무방향 그래프인 트리이기 때문에 크루스칼 알고리즘을 이용하여 $O(ElogE)$로 나오게 하겠습니다.
네트워크 연결 구현 코드
union-find 기법을 이용했습니다.
가중치를 오름차순으로 정렬하고 순차적으로 간선을 확인하며 같은 집합이 아닐시에 선택합니다.
package 네트워크연결_1922;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N, M;
static int[] parent;
static List<Route> adj;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
adj = new ArrayList<>();
parent = new int[1001];
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int C = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
adj.add(new Route(A, B, C));
}
Collections.sort(adj, Comparator.comparingInt(Route::getC));
int answer = 0;
for (Route curr : adj) {
if (isSameParent(curr.a, curr.b) == false) {
union(curr.a, curr.b);
answer += curr.c;
}
}
System.out.print(answer);
}
static void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot) return;
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
}
static int find(int a) {
if (parent[a] == a) return a;
else return parent[a] = find(parent[a]);
}
static boolean isSameParent(int a, int b) {
if (find(a) == find(b)) return true;
else return false;
}
}
class Route {
int a, b, c;
public Route(int a, int b, int c) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public int getC() {
return this.c;
}
}

댓글